
Can Hair Loss Be a Sign of Something Serious in Males?
Hair loss is a common concern among males, often leading to anxiety and reduced self-esteem. While hair loss can be a natural part of aging or a result of genetic predisposition, it can also signal underlying health issues. Understanding the various causes of hair loss is crucial for identifying when it might be a sign of something more serious.
Hair loss can range from mild thinning to complete baldness and can affect different parts of the scalp and body. For many men, hair loss is simply a cosmetic concern, but for others, it might indicate deeper health problems. Distinguishing between normal hair loss and hair loss that signals a medical condition is essential for appropriate intervention and treatment.
The purpose of this article is to explore the potential serious health issues that can be indicated by hair loss in males.will delve into the different causes and types of hair loss, and aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of when hair loss might require medical attention.
Affiliate Disclosure
As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases made through the links provided on this site. Rest assured, this won’t affect your cost in any way.
Hair Loss in Males
Hair loss in males can manifest in various forms, each with distinct causes and patterns.
Common Types of Hair Loss in Males
1. Androgenetic Alopecia (Male Pattern Baldness)
Androgenetic alopecia is the most common type of hair loss in men, affecting up to 80% of males by the age of 50. It is characterized by a receding hairline and thinning of the hair on the crown and temples.
Causes: This condition is primarily genetic and is influenced by hormones, particularly dihydrotestosterone (DHT), which causes hair follicles to shrink over time.
2. Alopecia Areata
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune disorder that causes sudden, patchy hair loss on the scalp, face, and sometimes other areas of the body.
Causes: The immune system mistakenly attacks hair follicles, leading to hair loss. The exact cause is unknown, but it is believed to be related to genetic and environmental factors.
3. Telogen Effluvium
Telogen effluvium is a temporary form of hair loss that occurs when a large number of hair follicles enter the resting (telogen) phase simultaneously, leading to shedding.
Causes: This condition is often triggered by stress, illness, surgery, or significant life changes. Nutritional deficiencies and certain medications can also contribute to telogen effluvium.
Normal Hair Loss vs. Excessive Hair Loss
Normal Hair Loss: On average, a person loses 50 to 100 hairs per day as part of the natural hair growth cycle. This type of hair loss usually goes unnoticed as new hairs grow to replace the lost ones.
Excessive Hair Loss: When hair loss exceeds this range or is accompanied by noticeable thinning or bald patches, it may be a sign of an underlying health issue. Excessive hair loss can manifest in different patterns, such as diffuse thinning, patchy bald spots, or a receding hairline, depending on the cause.
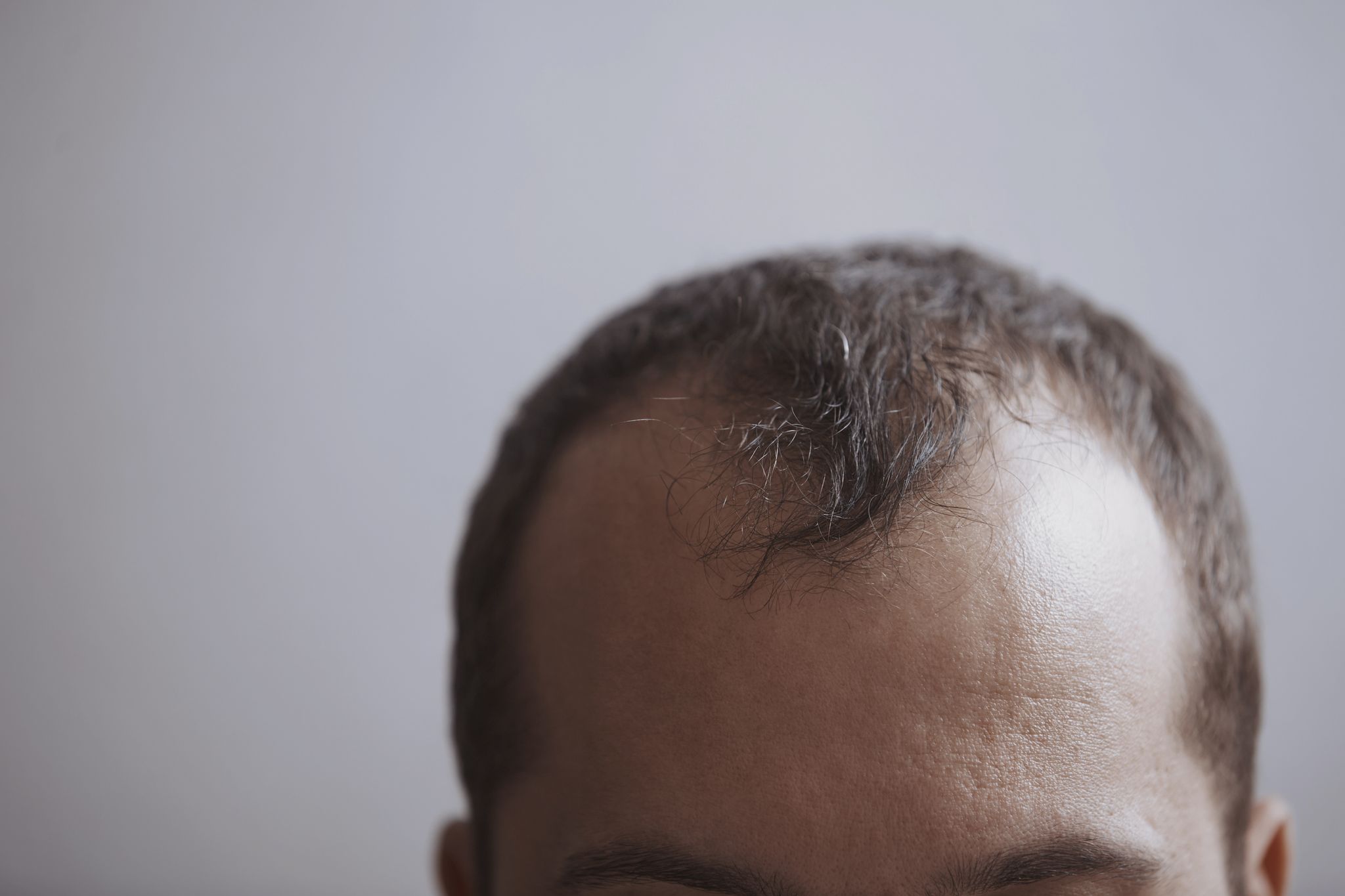
Common Causes of Hair Loss in Males
Genetic Factors
Hair loss in males can happen due to various reasons. One common cause is genetic factors. This means if your parents or grandparents had hair loss, you might also experience it. It happens because certain genes inherited from your family can make your hair follicles more sensitive to hormones like DHT, which can lead to hair loss.
Hormonal Changes
Hormonal changes can also play a big role in hair loss. For example, high levels of a hormone called dihydrotestosterone (DHT), which is related to testosterone, can shrink hair follicles and cause hair loss. Thyroid problems, like having an overactive or underactive thyroid, can also affect hair growth.
Aging
As men get older, it’s natural for hair growth to slow down. This happens because over time, hair follicles can stop producing new hairs, which can result in thinner hair or bald spots.
Lifestyle Factors
- Stress: High stress levels can push hair follicles into a resting phase, causing hair to fall out more easily.
- Diet: Poor nutrition, including lack of protein, vitamins, and minerals, can weaken hair and lead to hair loss.
- Health Habits: Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can damage hair follicles and lead to hair loss.
Hair Loss as a Potential Indicator of Serious Health Issues
While hair loss is often due to genetic factors or aging, it can sometimes be a sign of more serious health problems. Here are some conditions and factors to watch for:
Hormonal Imbalances
Hormonal changes can cause significant hair loss. Thyroid disorders, such as hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) and hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid), can disrupt the hair growth cycle. Also, high levels of hormones like dihydrotestosterone (DHT), which is related to testosterone, can shrink hair follicles and lead to hair loss.
Nutritional Deficiencies
Proper nutrition is crucial for healthy hair. A deficiency in iron, known as anemia, can cause hair loss because iron is essential for hair growth. Lack of protein in the diet can also weaken hair. Deficiencies in vitamins and minerals, such as Vitamin D, B12, and zinc, can lead to hair thinning and loss.
Autoimmune Diseases
Autoimmune diseases occur when the body’s immune system attacks its own cells. Lupus is an autoimmune disease that can cause hair to fall out in patches. Alopecia areata is another autoimmune condition where the immune system attacks hair follicles, leading to sudden hair loss.
Chronic Illnesses
Certain chronic illnesses can lead to hair loss. Diabetes can affect circulation and damage hair follicles. Heart disease can impact blood flow, which is essential for hair growth. Liver disease can disrupt the balance of nutrients and hormones needed for healthy hair.
Infections and Scalp Conditions
Scalp infections and skin conditions can also cause hair loss. Fungal infections, like tinea capitis, can invade the hair and scalp, leading to bald patches. Psoriasis, a skin condition that causes red, scaly patches, can affect the scalp and lead to hair loss. Seborrheic dermatitis, which causes oily, inflamed skin, can also damage hair follicles.
Medications and Treatments
Certain medications and treatments can lead to hair loss as a side effect. Chemotherapy, used to treat cancer, is well known for causing hair loss because it targets rapidly dividing cells, including hair follicles. Other medications, such as those for high blood pressure (hypertension) and depression, can also lead to hair loss in some individuals.
Diagnostic Approaches
If you experience sudden or excessive hair loss, it’s important to determine the cause. Here’s how you can approach diagnosing the issue:
When to See a Doctor
You should consider seeing a doctor if you notice:
- Sudden or rapid hair loss
- Bald patches
- Hair thinning
- Other symptoms like fatigue, weight changes, or skin issues
Initial Assessments
The first step usually involves a medical history and physical examination. Your doctor will ask about your hair loss pattern, family history, diet, stress levels, and any other symptoms you might have. They will also examine your scalp to look for signs of infection, inflammation, or other issues.
Diagnostic Tests
To pinpoint the exact cause of hair loss, your doctor may recommend several tests:
- Blood Tests: These tests can help identify nutritional deficiencies, thyroid problems, and other conditions that might be causing hair loss.
- Scalp Biopsy: In some cases, a small sample of scalp tissue is taken to examine under a microscope. This can help diagnose conditions like fungal infections or autoimmune diseases.
- Hormone Levels: Testing hormone levels, such as thyroid hormones and androgens like DHT, can reveal hormonal imbalances that may be contributing to hair loss.
Treatment and Management Options
Addressing Underlying Health Conditions
The first step in managing hair loss is to treat any underlying health issues. For instance, if hair loss is due to a thyroid problem, managing the thyroid condition can help restore hair growth. Similarly, addressing nutritional deficiencies through diet or supplements can improve hair health.
Medications and Topical Treatments
There are several medications and treatments available that can help manage hair loss:
- Minoxidil: This is a topical treatment that you apply directly to your scalp. It helps stimulate hair growth and slow down hair loss.
- Finasteride: This oral medication reduces DHT levels, which can help prevent hair follicles from shrinking and promote hair regrowth.
Lifestyle and Dietary Changes
- Balanced Diet: Ensure your diet is rich in essential nutrients like protein, iron, vitamins, and minerals. Foods like leafy greens, nuts, and lean proteins can be beneficial.
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of water keeps your hair and scalp hydrated.
Stress Management Techniques
Reducing stress can have a positive impact on hair health. Techniques such as meditation, yoga, regular exercise, and adequate sleep can help manage stress levels and improve overall well-being, which can, in turn, benefit your hair.
Hair Restoration Procedures
For those looking for more permanent solutions, there are several hair restoration procedures available:
- Hair Transplants: Involves moving hair follicles from one part of the body to the balding areas. This can provide natural-looking results and is often a long-term solution.
- Scalp Micropigmentation: A cosmetic procedure where tiny dots of pigment are tattooed on the scalp to give the appearance of fuller hair. This is a non-surgical option that can enhance the look of your hair.
 iRestore Essential Laser Hair Growth System – FDA Cleared Hair Loss Treatments for Men
iRestore Essential Laser Hair Growth System – FDA Cleared Hair Loss Treatments for Men
Preventive Measures
Preventing hair loss involves adopting healthy habits and routines that support overall hair health. Here are some key preventive measures:
Healthy Diet and Proper Nutrition
- Proteins: Essential for hair growth. Include lean meats, fish, eggs, and legumes.
- Vitamins and Minerals: Vitamins A, C, D, and E, along with minerals like iron, zinc, and biotin, are vital for hair health. Incorporate fruits, vegetables, nuts, and whole grains into your meals.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water to keep your scalp and hair hydrated.
Regular Medical Check-Ups
Regular visits to your doctor can help catch potential health issues early, including those that might affect your hair. Routine blood tests can detect nutritional deficiencies or hormonal imbalances that could lead to hair loss. Early intervention can prevent or reduce hair loss by addressing these issues promptly.
Stress Management
- Exercise: Regular physical activity helps reduce stress levels.
- Relaxation Techniques: Practices like meditation, yoga, and deep-breathing exercises can help manage stress.
- Adequate Sleep: Ensuring you get enough restful sleep each night supports overall health and well-being, including hair health.
Proper Hair Care Routine
- Gentle Washing: Use a mild shampoo and avoid washing your hair with hot water.
- Avoid Harsh Treatments: Limit the use of chemical treatments, heat styling tools, and tight hairstyles that can pull on your hair.
- Regular Trimming: Trim your hair regularly to avoid split ends and breakage.
- Scalp Care: Keep your scalp clean and healthy by gently massaging it during washing to promote blood circulation.
In summary, hair loss in males can result from various factors such as genetics, hormonal changes, aging, and lifestyle choices. It is important to understand that while hair loss can be a natural part of aging, it can also signal serious health issues like thyroid problems, nutritional deficiencies, autoimmune diseases, and chronic illnesses.
Early detection and treatment are crucial in managing hair loss effectively. If you experience sudden or unexplained hair loss, it is important to seek medical advice to identify the underlying cause and get appropriate treatment.
References
American Academy of Dermatology Association (AAD): Provides comprehensive information on various types of hair loss and their treatments.
Mayo Clinic: Offers detailed insights into the causes, symptoms, and treatments of hair loss.Hair Loss
National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases (NIAMS): Discusses autoimmune diseases like lupus and alopecia areata that cause hair loss.
Cleveland Clinic: Provides detailed information on the various causes of hair loss and available treatments.
Harvard Health Publishing: Discusses the impact of stress on hair loss and the importance of managing stress for overall health.Stress and Hair Loss: Are They Related?
Journal of Clinical and Diagnostic Research (JCDR): Contains studies on the effects of nutritional deficiencies on hair health.Study on Nutritional Deficiencies and Hair Loss
Endocrine Society: Discusses hormonal imbalances and their effects on hair loss.



Pingback: Side Effects of Applying Sugar on Hair - hair insight